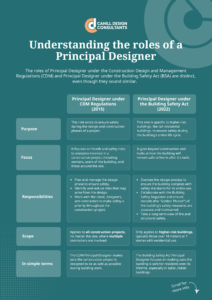
The roles of Principal Designer under the CDM Regulations and Principal Designer under the Building Safety Act are distinct, even though they sound similar.
| Principal Designer under CDM Regulations (2015) | Principal Designer under the Building Safety Act (2022) | |
| Purpose | This role exists to ensure safety during the design and construction phases of a project. | This role is specific to higher-risk buildings, like tall residential buildings, to ensure safety during the building’s entire life cycle. |
| Focus | It focuses on health and safety risks to everyone involved in a construction project, including workers, users of the building, and those around the site. | It goes beyond construction and looks at how the building will remain safe to live in after it’s built. |
| Responsibilities | – Plan and manage the design phase to ensure safety. – Identify and reduce risks that may arise from the design. – Work with the client, designers, and contractors to make safety a priority throughout the construction project. | – Oversee the design process to ensure the building complies with safety standards for its entire use. – Collaborate with the Building Safety Regulator and ensure records (the “Golden Thread”) of the building’s safety measures are accurate and maintained. – Take a long-term view of fire and structural safety. |
| Scope | Applies to all construction projects, no matter the size, where multiple contractors are involved. | Only applies to higher-risk buildings, typically those over 18 meters or 7 stories with residential use. |
| In Simple Terms | The CDM Principal Designer makes sure the construction project is designed to be as safe as possible during building work | The Building Safety Act Principal Designer focuses on making sure the building is safe for residents over its lifetime, especially in taller, riskier buildings. |
Key Difference
CDM Principal Designer: Ensures construction safety during design and building work.
Building Safety Act Principal Designer: Focuses on designing and maintaining long-term safety for residents in high-risk buildings.
Both roles are critical, but they address safety at different stages and for different purposes.
CDM Regs 2015
The CDM regulations were developed to help prevent construction accidents and fatalities, ensuring construction work is carefully planned so that risks are managed from start to finish.
The Building Safety Act 2022
The Building Safety Act 2022 amends the Building Act 1984 to: create powers to prescribe requirements on those who procure, design, plan, manage and undertake building work, introduce new enforcement powers for building control authorities.
It is a recent piece of legislation that came into force in October 2023, introduced by the government to enhance the safety and quality of residential buildings in the UK.
Its main goal is to tackle the systemic issues that caused the Grenfell Tower tragedy in 2017 by implementing measures to guarantee that buildings meet the highest safety standards, particularly tall and high-risk structures.
Download
CDC offer Building Safety Act Principal Designer services, whether it is full PD services across Gateways 1,2 and 3 or for Gateway 2 applications. The new legislation can seem quite daunting, we are here to help guide you through.
View our Building Safety Services here.